VTBS — Bangkok/ Suvarnabhumi International Airport
VTBS AD 2.1 AERODROME LOCATION INDICATOR AND NAME
VTBS — Bangkok/ Suvarnabhumi International Airport
VTBS AD 2.2 AERODROME GEOGRAPHICAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE DATA
| 1 |
ARP coordinates and site at AD |
134109N
1004456E
Midpoint between taxiways G, H, H2 and H3 |
| 2 |
Direction and distance from (city) | 25 KM East of Bangkok |
| 3 |
Elevation/Reference temperature | 4.2 FT (1.3 M) / 32.4°C |
| 4 | Geoid undulation at AD ELEV PSN | -97.5 FT (-29.7 M) |
| 5 |
MAG VAR/Annual change | 0° 35' W (2016) / 0° 0' E |
| 6 |
AD Administration, address, telephone, |
999 Moo 1 Nong Prue, Bangphli, Samut Prakan 10540, Thailand Tel: +662 132 1888 Fax: +662 132 1889 Website: https://suvarnabhumi.airportthai.co.th AFS: VTBSYDYX |
| 7 |
Types of traffic permitted (IFR/VFR) | IFR / Authorized VFR |
| 8 |
Remarks | Operator: Airports of Thailand Public Company Limited (AOT) |
VTBS AD 2.3 OPERATIONAL HOURS
| 1 |
Aerodrome operator | H24 |
| 2 |
Customs and immigration |
H24 |
| 3 |
Health and sanitation | H24 |
| 4 |
AIS Briefing Office | H24 |
| 5 |
ATS Reporting Office (ARO) | H24 |
| 6 |
MET Briefing Office | H24 |
| 7 |
ATS | H24 |
| 8 |
Fuelling | H24 |
| 9 |
Handling | H24 |
| 10 |
Security | H24 |
| 11 |
De-icing |
NIL |
| 12 |
Remarks |
AIS Briefing Office and ATS Reporting Office (ARO): |
VTBS AD 2.4 HANDLING SERVICES AND FACILITIES
| 1 |
Cargo-handling facilities | Available from Thai Airways International Plc.and WFS-PG Cargo Co., Ltd. (BFS Cargo) |
| 2 |
Fuel/oil types | Jet A1 |
| 3 |
Fuelling facilities/capacity |
|
| 4 |
De-icing facilities |
NIL |
| 5 |
Hangar space for visiting aircraft | Limited, operated by Thai Airways International Plc. |
| 6 |
Repair facilities for visiting aircraft |
Major and minor repair available from Thai Airways International Plc. and line maintenance from International Airlines Technical Pool. |
| 7 |
Remarks |
The Airport has provided ground handling agents as following:
|
VTBS AD 2.5 PASSENGER FACILITIES
| 1 |
Hotels | At AD and in the city. |
| 2 |
Restaurants | At AD and in the city. |
| 3 |
Transportation | Airport Rail Link, buses, taxis and car hire from the AD. |
| 4 |
Medical facilities |
Medical clinic which provides first aid and emergency response at AD is open 24 hours. Emergency number is +662 132 7777. |
| 5 |
Bank and Post Office | At AD. |
| 6 |
Tourist Office | At AD. |
| 7 |
Remarks |
For further information visit Internet address : |
VTBS AD 2.6 RESCUE AND FIRE FIGHTING SERVICES
| 1 |
AD category for fire fighting | Category 10 |
| 2 |
Rescue equipment | Adequately provided as recommended by ICAO |
| 3 |
Capability for removal of disabled aircraft |
Capable of handling all aircraft up to B744 dimensions & weight, operated by Thai Airways International Plc. |
| 4 |
Remarks |
For removal of disabled aircraft, please contact: Airside Operations Department |
VTBS AD 2.7 SEASONAL AVAILABILITY - CLEARING
| 1 |
Types of clearing equipment |
NIL |
| 2 |
Clearance priorities |
NIL |
| 3 |
Remarks | The AD is available all seasons. |
VTBS AD 2.8 APRONS, TAXIWAYS AND CHECK LOCATIONS/POSITIONS DATA
| 1 | Apron surface and strength |
Surface: Concrete Main Apron, East Apron and West Apron Strength: PCN 126/R/D/X/T SAT-1 Apron Strength: PCN 131/R/D/X/T | ||
| 2 | Taxiway width, surface and strength |
Minimum Width: 30 M Taxiways: B, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B10, B11, B12 and C, C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9 and C10 D (D1-D9), D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8 and D9 E, E1, E2, E5, E6, E7, E8, E9, E12, E13, E15, E17, E19 G H, H1, H2, H3 and H4 Taxilanes: T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T13, Surface: Asphalt Strength: PCN 137/F/D/X/T Taxiways: D (D9-D11), D10 and D11 J, J1, J2, J3 and J4 K Taxilanes: T18 and T19 Surface: Concrete Strength: PCN 131/R/D/X/T Taxiways: H5 and H6 Surface: Concrete Strength: PCN 131/R/D/X/T Surface: Asphalt Strength: PCN 137/F/D/X/T | ||
| 3 |
Altimeter checkpoint location and elevation |
Location : At Apron | ||
| 4 |
VOR checkpoints |
NIL | ||
| 5 |
INS checkpoints |
See Aircraft Parking/Docking Chart - ICAO (Versos) for coordinates of aircraft stand. | ||
| 6 |
Remarks |
NIL | ||
VTBS AD 2.9 SURFACE MOVEMENT GUIDANCE AND CONTROL SYSTEM AND MARKINGS
| 1 |
Use of aircraft stand ID signs, TWY guidelines and visual docking/parking guidance system of aircraft stands |
Taxiing guidance signs at all intersections with TWY and RWY and at all holding positions. Guidelines at apron. Nose-in guidance at aircraft stands. |
| 2 |
RWY and TWY markings and LGT |
RWY: Designation, THR, TDZ, Centre line, edge and runway end marked and lighted. TWY: Centre line and edge marked and lighted. |
| 3 |
Stop bars |
Stop bars are installed at following locations: - Taxiway B1, B2, B3, B11, B12, B13 - Taxiway E1, E2, E5, E15, E19, E21 |
| 4 |
Remarks | Intermediate holding positions are provided at some TWY/TWY intersections. |
VTBS AD 2.10 AERODROME OBSTACLES
|
In approach/TKOF areas |
In circling areas and at AD |
Remarks | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|
RWY/Area affected |
Obstacle type Elevation Markings/LGT |
Coordinates |
Obstacle type Elevation Markings/LGT |
Coordinates | |
| a | b | c | a | b | |
|
19R/APCH 01L/TKOF |
|
Control Tower Top of Antenna 475.4 FT (144.9 M) LGTD |
134147.2N
1004458.3E
|
NIL | |
|
|
Tower on top of building 178.2 FT (54.3 M) LGTD |
134124.1N
1004346.5E
| |||
|
01L/APCH 19R/TKOF |
Tower on top of building 174.6 FT (53.2 M) LGTD |
133808.2N
1004340.2E
|
Tower 160.8 FT (49.0 M) LGTD |
133943.8N
1004259.5E
|
NIL |
|
Tower on top of building 179.8 FT (54.8 M) LGTD |
133751.8N
1004354.2E
|
Tower on top of building 191.0 FT (58.2 M) LGTD |
133810.0N
1004233.7E
| ||
|
|
Tower 381.9 FT (116.4 M) LGTD |
133802.9N
1004217.7E
| |||
|
|
Tower 300.5 FT (91.6 M) LGTD |
133747.5N
1004226.1E
| |||
|
|
Tower 160.8 FT (49.0 M) LGTD |
133806.3N
1004237.6E
| |||
|
19L/APCH 01R/TKOF |
Tower on top of building 256.3 FT (78.1 M) LGTD |
134339.8N
1004620.6E
|
|
NIL | |
|
Tower 145.7 FT (44.4 M) LGTD |
134316.9N
1004549.8E
|
| |||
|
Hangar roof 153.2 FT (46.7 M) LGTD |
134224.7N
1004534.8E
|
| |||
|
Hangar corner 130.3 FT (39.7 M) LGTD |
134222.0N
1004538.9E
|
| |||
|
Tower on top of building 160.4 FT (48.9 M) LGTD |
134332.3N
1004617.2E
|
| |||
|
01R/APCH 19L/TKOF |
Building 334.0 FT (101.8 M) LGTD |
133512.8N
1004425.7E
|
NIL | ||
|
Tower 350.1 FT (106.7 M) LGTD |
133458.3N
1004430.7E
|
| |||
|
Tower 389.5 FT (118.7 M) LGTD |
133458.1N
1004429.0E
|
| |||
VTBS AD 2.11 METEOROLOGICAL INFORMATION PROVIDED
| 1 |
Associated MET Office | Aeronautical Meteorology Division, Thai Meteorological Department (TMD) |
| 2 |
Hours of service MET Office outside hours |
H24 NIL |
| 3 |
Office responsible for TAF preparation Periods of validity | Aeronautical Meteorology Division 30 HR |
| 4 |
Trend forecast Interval of issuance |
TREND
30 Min |
| 5 |
Briefing/consultation provided |
Personal Consultation Tel: +662 134 0006-07 Fax: +662 134 0009 |
| 6 |
Flight documentation Language(s) used |
Charts, Tabular Forms and Abbreviated Plain Language Texts English |
| 7 |
Charts and other information available for | S, U85, U70, U50, U40, U30, U25, U20, SWH, SWM, SWL, P85, P70, P50, P40, P30, P25, P20, P15, satellite and radar pictures |
| 8 |
Supplementary equipment available for | Automated Weather Observation System (AWOS), Low Level Wind Shear Alert System (LLWAS), Weather Radar, Local Lightning Warning System (LLWS), Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) |
| 9 |
ATS units provided with information |
Suvarnabhumi TWR Bangkok APP Bangkok ACC |
| 10 |
Additional information (limitation of service, etc.) |
NIL |
VTBS AD 2.12 RUNWAY PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
|
Designations RWY NR |
TRUE BRG |
Dimensions of RWY(M) | Strength (PCN) and surface of RWY and SWY |
THR coordinates RWY end coordinates THR geoid undulation | THR elevation and highest elevation of TDZ of precision APP RWY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 01L | 014.42° | 3700x60 |
PCN 137/F/D/X/T Asphalt |
134016.60N
1004404.79E
-97.5 FT (-29.7 M) | THR/TDZ 4.2 FT (1.3 M) |
| 19R | 194.42° | 3700x60 |
PCN 137/F/D/X/T Asphalt |
134213.21N
1004435.44E
-97.5 FT (-29.7 M) | THR/TDZ 4.0 FT (1.2 M) |
| 01R | 014.42° | 4000x60 |
PCN 137/F/D/X/T Asphalt |
133924.11N
1004506.59E
-97.1 FT (-29.6 M) | THR/TDZ 3.7 FT (1.1 M) |
| 19L | 194.42° | 4000x60 |
PCN 137/F/D/X/T Asphalt |
134130.17N
1004539.72E
-97.1 FT (-29.6 M) |
THR/TDZ 3.7 FT (1.1 M) |
| Slope of RWY-SWY |
SWY dimensions (M) | CWY dimensions (M) | Strip dimensions (M) | RESA dimensions (M) | Location and description of arresting system | OFZ | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | ||
| 0% | NIL | 1100x150 | 3820x300 | 240x150 |
NIL |
Yes |
Paved jet blast protection areas at runway ends; 120 M long and 75 M wide. Runway 01L/19R surface is grooved; Runway 01R/19L surface is not grooved. Concrete drainage channels are located in the runway strips, parallel to and at 120 M offset from the runway centre lines . | ||
| 0% | NIL | 700x150 | 3820x300 | 240x150 |
NIL |
Yes | |||
| 0% |
NIL |
NIL | 4120x300 | 240x150 |
NIL |
Yes | |||
| 0% |
NIL | 550x150 | 4120x300 | 240x150 |
NIL |
Yes | |||
VTBS AD 2.13 DECLARED DISTANCES
|
RWY Designator |
TORA (M) |
TODA (M) |
ASDA (M) |
LDA (M) |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 01L | 3700 | 4800 | 3700 | 3700 | The TORA/ASDA when entering RWY from TWY E19 is 3590 M. |
| 19R | 3700 | 4400 | 3700 | 3700 | The TORA/ASDA when entering RWY from TWY E2 is 3590 M. |
| 01R | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | The TORA/ASDA when entering RWY from TWY B12 is 3890 M. |
| 19L | 4000 | 4550 | 4000 | 4000 | The TORA/ASDA when entering RWY from TWY B2 is 3870 M. |
VTBS AD 2.14 APPROACH AND RUNWAY LIGHTING
|
RWY Designator |
APCH LGT type LEN INTST |
THR LGT colour WBAR |
VASIS (MEHT) PAPI |
TDZ, LGT LEN |
RWY Centre Line LGT Length, spacing, colour, INTST |
RWY edge LGT LEN, spacing, colour INTST |
RWY End LGT colour WBAR |
SWY LGT LEN (M) colour |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 01L |
CAT II 900 M 5 steps LIH; with FLG | Green |
PAPI LEFT/3° (63.82 FT) | 900 M |
3700 M, 30 M White, FM 2800 M Red / White FM 3400 M Red 5 steps LIH |
3700 M, 60 M White, FM 3100 M Yellow 5 steps LIH | Red |
NIL |
NIL |
| 19R |
CAT II 900 M 5 steps LIH; with FLG | Green |
PAPI LEFT/3° (63.82 FT) | 900 M |
3700 M, 30 M White, FM 2800 M Red / White FM 3400 M Red 5 steps LIH |
3700 M, 60 M White, FM 3100 M Yellow 5 steps LIH | Red |
NIL |
NIL |
| 01R |
CAT II 900 M 5 steps LIH; with FLG | Green |
PAPI LEFT/3° (63.82 FT) | 900 M |
4000 M, 30 M White, FM 3100 M Red/White FM 3700 M, Red 5 steps LIH |
4000 M, 60 M White, FM 3400 M Yellow 5 steps LIH | Red |
NIL |
NIL |
| 19L |
CAT II 900 M 5 steps LIH; with FLG | Green |
PAPI LEFT/3° (63.82 FT) | 900 M |
4000 M, 30 M White, FM 3100 M Red/White FM 3700 M, Red 5 steps LIH |
4000 M, 60 M White, FM 3400 M Yellow 5 steps LIH | Red |
NIL |
NIL |
VTBS AD 2.15 OTHER LIGHTING, SECONDARY POWER SUPPLY
| 1 |
ABN/IBN location, characteristics and hours of operation |
ABN: On top of ATC tower (134147N 1004458E), H24, Flashing White/Green every 2 - 3 seconds IBN: NIL |
| 2 |
LDI location and LGT Anemometer location and LGT |
4 WDIs 300 M from THR 01L, THR 19R, THR 01R, THR 19L, 115 M off-set from RWY Centre Line. All Lighted. 4 Anemometers 350 M from THR 01L, THR 19R, THR 01R, THR 19L and Lighted. |
| 3 |
TWY edge and centre line lighting | All Taxiways |
| 4 |
Secondary power supply/switch-over time |
Secondary power supply to all airfield lighting at AD Switch-over time: Lights Associated to Runway 0 sec (UPS) include - Approach Lights Systems - Runway Edge Lights - Runway Touchdown Zone Lights - Runway Centre Line Lights - Precision Approach Path Indicator Systems - Stop Bars - Runway Guard Lights - Runway End Lights - Runway Threshold Lights : Other lighting 15 sec |
| 5 |
Remarks |
NIL |
VTBS AD 2.16 HELICOPTER LANDING AREA
| 1 |
Coordinates TLOF or THR of FATO Geoid undulation |
NIL |
| 2 |
TLOF and/or FATO elevation M/FT |
NIL |
| 3 |
TLOF and FATO area dimensions, surface, strength, marking |
NIL |
| 4 |
True BRG of FATO |
NIL |
| 5 |
Declared distance available |
NIL |
| 6 |
APP and FATO lighting |
NIL |
| 7 |
Remarks |
NIL |
VTBS AD 2.17 ATS AIRSPACE
| 1 |
Designation and lateral limits |
Suvarnabhumi Aerodrome Traffic Zone (ATZ) a circle, radius 5 NM centred on 134108.59N 1004456.24E (ARP) |
| 2 |
Vertical limits | SFC to 2000 FT. MSL |
| 3 |
Airspace classification | C |
| 4 |
ATS unit call sign Language(s) |
Suvarnabhumi Tower English, Thai |
| 5 |
Transition altitude | 11000 FT MSL |
| 6 |
Remarks | See VTBS AD 2.20 section 1 |
VTBS AD 2.18 ATS COMMUNICATION FACILITIES
|
Service designation |
Call sign |
Frequency |
Hours of operation |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| APP | Bangkok Approach |
122.35 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 124.35 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 125.2 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 133.4 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 119.1 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 120.3 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 125.8 MHZ2) 121.5 MHZ1) / 243 MHZ1) | H24 |
1)Emergency frequency 2)Clearance delivery for aircraft departing to adjacent aerodromes and helicopters operating within BKK CTR 3)For RWY 01R/19L 4)For RWY 01L/19R 5)Arrival ATIS 6)Departure ATIS |
| APP | Suvarnabhumi Departure |
119.25 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 121.5 MHZ1) / 243.0 MHZ1) | H24 | |
| ARR | Suvarnabhumi Arrival |
121.1 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 126.3 MHZ / 262.5 MHZ 121.5 MHZ1) / 243.0MHZ1) | H24 | |
| TWR | Suvarnabhumi Tower |
118.2 MHZ3) / 274.5 MHZ 119.0 MHZ4) 121.5 MHZ1) / 243.0 MHZ1) | H24 | |
| SMC | Suvarnabhumi Ground |
121.65 MHZ / 275.8 MHZ 121.75 MHZ 121.95 MHZ | H24 | |
| Suvarnabhumi Delivery |
128.7 MHZ 133.8 MHZ | H24 | ||
| ATIS | Suvarnabhumi Airport |
133.6 MHZ5)/ 278.6 MHZ5)/ 127.65 MHZ6) | H24 |
D-ATIS Synthesis Voice Broadcast |
VTBS AD 2.19 RADIO NAVIGATION AND LANDING AIDS
|
Type of aid, MAG VAR CAT of ILS/MLS (For VOR/ILS/MLS, give declination) |
ID |
Frequency | Hours of operation |
Position of transmitting antenna coordinates |
Elevation of DME transmitting antenna |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| DVOR/DME | SVB |
111.4 MHZ CH 51X | H24 |
133932.5N
1004353.2E
| - |
DVOR/DME restriction due to terrain surround DVOR/DME station, coverage check does not provide adequate signal 40 NM at required altitude in various areas as follows:
|
|
ILS CAT II LOC/DME RWY 01L | I-SWS |
109.1 MHZ CH 28X | H24 |
134222.3N
1004437.8E
| - |
RWY 01L/19R and RWY01R/19L ILS LOC coverage expanded service volume up to 25 DME altitude not below 2 500 FT AMSL. |
|
GP |
331.4 MHZ | H24 |
134027.8N
1004403.6E
| - | ||
|
ILS CAT II LOC/DME RWY 19R | I-SWN |
109.5 MHZ CH 32X | H24 |
134007.5N
1004402.4E
| - | |
| GP | 332.6 MHZ | H24 |
134203.9N
1004428.9E
| - | ||
|
ILS CAT II LOC/DME RWY 01R | I-SES |
110.1 MHZ CH 38X | H24 |
134139.3N
1004542.1E
| - | |
| GP | 334.4 MHZ | H24 |
133933.4N
1004513.1E
| - | ||
|
ILS CAT II LOC/DME RWY 19L | I-SEN |
110.5 MHZ CH 42X | H24 |
133915.0N
1004504.2E
| - | |
| GP | 329.6 MHZ | H24 |
134119.0N
1004540.9E
| - |
VTBS AD 2.20 LOCAL AERODROME REGULATIONS
1. Airport Regulations
a search and rescue operation;
a medical emergency; or
a flight inspection of air navigation facilities.
school and training flights;
continuous take-off and landing exercises;
solo flight during basic flight training.
2. Provision of Aerodrome Air Traffic Services
Aircraft parking stands:
A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6
C1, C3, C5, C7, C9
101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134
201, 202, 203
Including:
Taxiway B, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, B8, B9, B10, B11, B12, B13
Taxiway C, C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9, C10
Taxiway G between taxiway C and taxiway H4
Taxiway H between taxiway C and taxiway H4
Taxiway H4
Aircraft stand taxilane T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7
Aircraft parking stands:
C2, C4, C6, C8, C10
D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8
E1, E3, E5, E7, E9
301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 308
S101, S102, S103, S104, S105, S106, S107, S108, S109, S110, S111, S112, S113, S114,
S115, S116, S117, S118, S119, S120, S121, S122, S123, S124, S125, S126, S127, S128
Including:
Taxiway G between taxiway H2 and taxiway H4
Taxiway H2, H3, H5, H6
Taxiway J1, J2
Aircraft stand taxilane T8, T9, T10, T11, T12, T18, T19
Aircraft parking stands:
E2, E4, E6, E8, E10
F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6
G1, G2, G3, G4, G5
401, 402, 403
501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525
Including:
Taxiway D, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, D10, D11
Taxiway E, E1, E2, E5, E6, E7, E8, E9, E12, E13, E15, E17, E19, E21
Taxiway G between taxiway D and taxiway H2
Taxiway H between taxiway D and taxiway H4
Taxiway H1
Taxiway J, J3, J4
Taxiway K
Aircraft stand taxilane T13, T14, T15, T16, T17
3. Ground Movement
for a departing flight, upon received airway clearance; except that subject to ATFM measures or departure time restrictions, the action should be done when starting up engine.
for an arriving flight, continuously until the aircraft is fully parked at the stand.
for departure, when aircraft are entering the runway or line up clearance is received;
for arrival, until aircraft have vacated the runway.
for departure, when starting up engine;
for arrival, until aircraft have completely parked.
To provide tracking and identification of authorized movements, any authorized vehicle intended to be used on the manoeuvring area at Suvarnabhumi International Airport shall be equipped with mode S squitter box to inform mode S multilateration system of its position.
4. Push Back Procedures
The procedure covers and details the activities to be carried out by ATC staff, AOT staff and airport agencies staff when involved in the process of an aircraft start up and push back at Suvarnabhumi International Airport.
Note: fully ready in this sense means all passengers, hold and cargo doors are closed, the Passenger Loading Bridge is disconnected and back in its rest position, the tug is connected to the aircraft and the ground engineer is in position and in contact with the pilot-in-command.
| Aircraft stands | Frequency Ground Control | Push Back Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| A1, A2 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft standtaxilane T5 until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| A3, A4, A5, A6 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5. |
| 101 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5. |
| 115, 116, 117 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5. |
| 118 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
119, 120,121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5. |
| 130 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T1. |
| 131, 132, 133 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T1, towed forward until abeam stand 131. |
| 134 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T5. |
| B1, B3 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T5 until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| B2, B4 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T6 until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane. |
| B5 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T4 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane. |
| B6 | 121.65 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T6 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane. |
| C1 | 121.65 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T6 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane.. |
| C3, C5 | 121.65 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T7 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| C7, C9 | 121.65 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T7 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 201, 202 | 121.65 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T7 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| 203 | 121.65 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T7 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| Aircraft stands | Frequency Ground Control | Push Back Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| C2 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| C4, C6 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T8 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| C8, C10 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T8 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 301 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T9 until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 302 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T9 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 303 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T9 until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| 304 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T9 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| 305 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T10 until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 306 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T10 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 307 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T10 until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| 308 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T10 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| D1 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| D2 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| D3 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| D4 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| D5 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 3. |
| D6 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 until nose wheel is on marking 3. |
| D7 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 4. |
| D8 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 until nose wheel is on marking 4. |
| E1 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T12 until nose wheel is on marking 4. |
| E3, E5 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T11 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| E7, E9 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T11 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| Aircraft stands | Frequency Ground Control | Push Back Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| E2 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T14 until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane |
| E4, E6 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T13 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| E8, E10 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T13 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 401, 402 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T13 until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| 403 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto aircraft stand taxilane T13 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| F1, F3 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T14 until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane |
| F5 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T14 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane |
| F2, F4 | 121.95 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T15 until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane. |
| F6 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T15 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane. |
| G1, G2 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T15 until nose wheel is on marking on taxilane |
| G3, G4 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T17 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| G5 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T17 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 501 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T17 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 502, 503 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T17 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 2. |
| 504, 505 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face north onto aircraft stand taxilane T17 then towed forward until nose wheel is on marking 1. |
| 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto taxiway D. |
| 522, 523, 524, 525 | 121.95 MHZ | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face south onto taxiway D, then towed forward until abeam stand 522 with nose wheel is on marking on taxiway. |
4.4.4 Aircraft parking at SAT-1 Apron (28 stands)
| Aircraft Stands | Ground Control Frequency | Push Back Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| S101 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S102 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S103 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S104 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S105 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S106 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S107 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S108 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S109 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S110 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S111 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S112 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S113 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S114 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S115 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S116 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S117 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S118 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S119 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S120 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face west onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S121 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S122 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S123 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S124 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S125 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S126 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
| S127 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T18. |
| S128 | 121.75 MHz | Aircraft shall be pushed back to face east onto aircraft stand taxilane T19. |
When the aircraft is fully ready the pilot-in-command is responsible to obtain the start-up and push back permission, stating the parking position.
The ground engineer of the Airline or Ground Handling Agent is responsible for a safe process of aircraft start up and push back and to report to the pilot-in-command when he/she and the tug are clear of the taxiway in the event of low visibility condition.
The tug driver is responsible to ensure that the aircraft is pushed back (and pulled forward if required) toward the right direction onto the taxilane.
The Apron Controller is responsible to monitor the engine start up and push back activities and to ensure that the aircraft will be pushed back toward the right direction onto the taxilane.
When the aircraft is fully ready the pilot-in-command shall:
Ensure that the area behind an aircraft is clear of vehicles, equipment and other obstructions before the start-up or push back of aircraft commences. This is to be done using standard phraseology in communication with the ground operations headset operator.
Ensure that prior to the start-up, the pilot shall be certain that the propellers or the air flows caused by the engine cannot cause injuries or damage to persons or properties on ground. This is to be done by using standard phraseology in communication with the ground operations headset operator.
Contact Ground Control for permission to start up the engine(s). In normal operations, the engine start-up at the aircraft parking position is not allowed.
Ensure that the ground engineer, or the person responsible for ground to cockpit communications who is in direct intercom-radio contact with the pilot-in-command, acknowledges the start-up permission. In the event intercom-radio contact is not available, the use of standard hand signals will be used.
Ensure that the anti-collision beacons of the aircraft have been switched on before pushing back or starting the engine and to obtain an “all-clear” signal from the ground operations headset operator.
During push back operations, all aircraft shall be pushed back with its fuselage longitudinally centred over, and parallel to, a taxiway centre line before commencing the engine start. Should the engine start be performed at the aircraft parking positions, ensure that the requirements for such engine start up conditions are met.
Ensure that the ground engineer or ground operations headset operator acknowledges the permission.
Ensure that the aircraft is being pushed back in the right direction onto the taxilane.
Request permission from Ground Control to taxi when the tug has been disconnected as confirmed by the ground engineer and the ground engineer or ground operations headset operator has given the “all clear” signal .
The ground engineer of the Airline or Handling Agent shall:
Ensure that the stand area is clear of any obstacle and FOD.
Ensure that the tug is connected to the aircraft and that the tug driver is completely ready to perform the push-back.
Acknowledge the Ground Control permission to start up the engine(s) to the pilot-in-command.
Ensure that the anti-collision beacons of the aircraft are switched on.
Monitor the engine(s) start up sequence.
Acknowledge the Ground Control permission for push back to the pilot-in-command.
Ensure that the tug driver understood the push back permission (by hand -signaling to the tug driver) and starting the push back manoeuvre.
Ensure that the aircraft is pushed back toward the right direction onto the taxilane.
Make sure that during the push back manoeuvre he/she will be in contact with the pilot-in-command at all times.
Ensure that the tug has been disconnected from the aircraft on the taxilane stop position and confirm so to the pilot-in-command.
When disconnected from the radio contact with the pilot-in-command, give the “all clear” signal to the pilot-in-command, being well clear of the aircraft’s path of taxiing.
Return to the stand area.
During low visibility conditions (CAT II) the ground engineer will, together with the tug driver, return behind the double white marking line on the apron surface as soon as possible and will indicate to the pilot-in-command that both of them are clear of the taxiway.
Note: CAT II: Runway Visual Range of less than 550 M or cloud base of less than 200 FT.
The tug driver of the Airline or Handling Agent shall:
Ensure that the tug is properly connected to the aircraft
Start the push back manoeuvre when permission to do so has been given by the ground engineer.
Make sure that the aircraft is pushed back toward the right direction onto the taxilane stop position.
Disconnect the tug from the aircraft when in position on the taxilane.
Return to the stand area.
During low visibility conditions (CAT II) the tug driver will, together with the ground engineer, return behind the red clearance line marking on the apron surface as soon as possible.
Note: CAT II: Runway Visual Range of less than 550 M or cloud base of less than 200 FT.
The Apron Controller will:
Monitor the engine(s) start up and push back activities.
Ensure that the aircraft will be pushed back toward the right direction onto the taxilane.
5. Taxi Procedures
a) holding position;
b) runway designator;
c) taxi routes;
d) any other pertinent information.
For example:
“…C/S… TAXI TO HOLDING POINT RUNWAY ONE NINE LEFT VIA TANGO FOUR, CHARLIE, CHARLIE THREE, BRAVO ONE.”
a) taxi routes;
b) parking stand;
c) any other pertinent information.
For example:
“…C/S… TAXI VIA ECHO, DELTA SEVEN, GOLF, TANGO ONE ZERO, TANGO ONE TWO, YOUR STAND DELTA SIX.”
the taxi-out position of an aircraft and runway-in-use. The clearance limit shall be at the holding position of runway- in-use.
For example:
“…C/S... TAXI VIA ROUTE ECHO TANGO FOUR, RUNWAY ONE NINE LEFT.”
For example:
“…C/S…TAXI VIA ROUTE ONE NINE RIGHT, MIKE TANGO ONE ZERO, YOUR STAND DELTA SIX.”
a) the departing aircraft reaches the holding position of active runway;
b) the arriving aircraft, completely parks at the assigned stand.
Pilots are reminded that, in no case shall the taxi instruction received on initial contact be altered, except approved otherwise specified by ATC.
with taxilane T8 and the markings T10A and T10B connect taxilane T10 with taxilane T11 are provide. The routes may only be used when instructed to do so by ATC (ATC discretion).
5.6.1 Inbound taxi route runway 19R
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | EAST | 19R/ET3 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T3, T5 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T3, T5, T4 | B1, B3, B5 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T3, T5, T1 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | ||||||
| 19R / ET6 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T6 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T6, T7 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | MAIN | 19R / MT9 | EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T9 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | |||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T9, T12 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T9, T12, T8 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | ||||||
| 19R / MT10 | EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T10 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T10, T12 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T10, T12, T11 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | WEST | 19R / WD1 | EXIT ONTO E, D1, D | 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| 19R / WD3 | EXIT ONTO E, D3, D | 506, 507, 508, 509 | |||||
| 19R / WT14 | EXIT ONTO E, D6, T14, T13 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D6, T14 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| 19R / WT15 | EXIT ONTO E, D5, T15 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D5, T15, T17 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | SAT-1 | 19R / SH5 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, H5, T18 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| 19R / SH6 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, H6, T18 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| 19R / SJ1 | EXIT ONTO E, D11, K, J3, J1, T19 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| 19R / SJ2 | EXIT ONTO E, D11, K, J4, J2, T19 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | EAST | 19L / ET3 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, T3, T5 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6,101, 102, 103, 104, 105,106, 107, 108, 109,110, 111, 112, 113, 114,115, 116, 117, 118, 119,120, 121, 122, 123, 124,125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, T3, T5, T4 | B1, B3, B5 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, T3, T5, T1 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | ||||||
| 19L / ET6 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, T6 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, T6, T7 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | MAIN | 19L / MT9 | EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T9 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | |||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T9, T12 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T9, T12, T8 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | ||||||
| 19L / MT10 | EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T10 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T10, T12 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T10, T12, T11 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | WEST | 19L / WD1 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D1, D | 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| 19L / WD3 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D3, D | 506, 507, 508, 509 | |||||
| 19L / WT14 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D6, T14, T13 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D6, T14 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| 19L / WT15 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D5, T15 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D5, T15, T17 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | SAT-1 | 19L / SH5 | EXIT ONTO B, C10, C, H, H5, T18 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| 19L / SH6 | EXIT ONTO B, C10, C, H, H6, T18 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| 19L / SJ1 | EXIT ONTO B, C10, C, K, J3, J1, T19 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| 19L / SJ2 | EXIT ONTO B, C10, C, K, J4, J2, T19 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | EAST | 01R/ET3 | EXIT ONTO B, C2, T3, T5 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||
| EXIT ONTO B, C2, T3, T5, T4 | B1, B3, B5 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C2, T3, T5, T1 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | ||||||
| 01R / ET6 | EXIT ONTO B, C5, T6 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C5, T6, T7 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | MAIN | 01R / MT9 | EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T9, T12, T8 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | |||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T9, T12 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T9 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | ||||||
| 01R / MT10 | EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T10, T12, T11 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T10, T12 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C6, G, T10 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | WEST | 01R / WD1 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D1, D | 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| 01R / WD3 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D3, D | 506, 507, 508, 509 | |||||
| 01R / WT14 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D6, T14, T13 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D6, T14 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| 01R / WT15 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D5, T15 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, D8, E, D5, T15, T17 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | SAT-1 | 01R / SH5 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, H5, T18 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| 01R / SH6 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, H, H6, T18 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| 01R / SJ1 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, K, J3, J1, T19 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| 01R / SJ2 | EXIT ONTO B, C7, C, K, J4, J2, T19 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | EAST | 01L / ET3 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T3, T5 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T3, T5, T4 | B1, B3, B5 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T3, T5, T1 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | ||||||
| 01L / ET6 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T6 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, C, T6, T7 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | MAIN | 01L / MT9 | EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T9, T12, T8 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | |||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T9, T12 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T9 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | ||||||
| 01L / MT10 | EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T10, T12, T11 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T10, T12 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D7, G, T10 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | WEST | 01L / WD1 | EXIT ONTO E, D1, D | 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| 01L / WD3 | EXIT ONTO E, D3, D | 506, 507, 508, 509 | |||||
| 01L / WT14 | EXIT ONTO E, D6, T14, T13 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D6, T14 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| 01L / WT15 | EXIT ONTO E, D5, T15 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D5, T15, T17 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | SAT-1 | 01L / SH5 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, H5, T18 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| 01L / SH6 | EXIT ONTO E, D8, H, H6, T18 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| 01L / SJ1 | EXIT ONTO E, D11, K, J3, J1, T19 (for aircraft exit via E1, E2, E5, E7) | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, D, K, J3, J1, T19 (for aircraft exit via E12) | |||||||
| 01L / SJ2 | EXIT ONTO E, D11, K, J4, J2, T19 (for aircraft exit via E1, E2, E5, E7) | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EXIT ONTO E, D8, D, K, J4, J2, T19 (for aircraft exit via E12) | |||||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | EAST | ET1 / 19R | T1, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | |||
| ET2 / 19R | T5, T2, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||||
| ET4 / 19R | T4, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | B1, B3, B5 | |||||
| T5, T4, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123 | ||||||
| ET7 / 19R | T6, T7, H4, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| T7, H4, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | MAIN | MT8 / 19R | T8, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | |||
| T12, T8, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| T9, T12, T8, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | ||||||
| MT11 / 19R | T11, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | |||||
| T12, T11, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| T10, T12, T11, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | WEST | WD2 / 19R | D, D2 TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| WD4 / 19R | D, D4, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | 506, 507, 508, 509, 510 | |||||
| WT13 / 19R | T13, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| T14, T13, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| WT16 / 19R | T15, T17, T16, D4, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| T17, T16, D4, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19R | SAT-1 | SH5 / 19R | T18, H5, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| SH6 / 19R | T18, H6, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| SJ1 / 19R | T19, J1, J, D10, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| SJ2 / 19R | T19, J2, J, D10, E TO HOLDING POSITION E1 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | EAST | ET1 / 19L | T1, C, C2, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | |||
| ET2 / 19L | T5, T2, C, C2, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||||
| ET4 / 19L | T4, C, C3, TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | B1, B3, B5 | |||||
| T5, T4, C, C3, TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123 | ||||||
| ET7 / 19L | T6, T7, G, C6, B HOLDING POSITION B1 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| T7, G, C6, B HOLDING POSITION B1 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | MAIN | MT8 / 19L | T8, G, C6, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | |||
| T12, T8, G, C6, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| T9, T12, T8, G, C6, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | ||||||
| MT11 / 19L | T11, G, C6, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | |||||
| T12, T11, G, C6, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| T10, T12, T11, G, C6, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | WEST | WD / 19L | D, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| WT13 / 19L | T13, H1, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| T14, T13, H1, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| WT16 / 19L | T15, T17, T16, D, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| T17, T16, D, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 19L | SAT-1 | SH5 / 19L | T18, H5, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| SH6 / 19L | T18, H6, H, C7, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| SJ1 / 19L | T19, J1, J, C9, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| SJ2 / 19L | T19, J2, J, C9, B TO HOLDING POSITION B1 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | EAST | ET1 / 01R | T1, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | |||
| ET2 / 01R | T5, T2, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||||
| ET4 / 01R | T4, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | B1, B3, B5 | |||||
| T5, T4, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123 | ||||||
| ET7 / 01R | T6, T7, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| T7, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | MAIN | MT8 / 01R | T8, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | |||
| T12, T8, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| T9, T12, T8, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | ||||||
| MT11 / 01R | T11, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | |||||
| T12, T11, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| T10, T12, T11, G, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | WEST | WD / 01R | D, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| WT13 / 01R | T13, H1, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| T14, T13, H1, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| WT16 / 01R | T15, T17, T16, D, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| T17, T16, D, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01R | SAT-1 | SH5 / 01R | T18, H5, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| SH6 / 01R | T18, H6, H, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| SJ1 / 01R | T19, J1, J, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| SJ2 / 01R | T19, J2, J, C, C10, B TO HOLDING POSITION B13 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
| EAST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | EAST | ET1 / 01L | T1, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | 130, 131, 132, 133, 134 | |||
| ET2 / 01L | T5, T2, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | 108, 109, 110, 111, 112, 113, 114, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129 | |||||
| ET4 / 01L | T4, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | B1, B3, B5 | |||||
| T5, T4, C, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123 | ||||||
| ET7 / 01L | T6, T7, H4, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | B2, B4, B6 | |||||
| T7, H4, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | C1, C3, C5, C7, C9, 201, 202, 203 | ||||||
| MAIN APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | MAIN | MT8 / 01L | T8, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | C2, C4, C6, C8, C10 | |||
| T12, T8, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | D1, D2, D3, D4 | ||||||
| T9, T12, T8, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | 301, 302, 303, 304 | ||||||
| MT11 / 01L | T11, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | E1, E3, E5, E7, E9 | |||||
| T12, T11, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | D5, D6, D7, D8 | ||||||
| T10, T12, T11, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | 305, 306, 307, 308 | ||||||
| WEST APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | WEST | WD / 01L | D, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525 | |||
| WT13 / 01L | T13, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | E2, E4, E6, E8, E10, 401, 402, 403 | |||||
| T14, T13, G, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | F1, F3, F5 | ||||||
| WT16 / 01L | T15, T17, T16, D, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | F2, F4, F6 | |||||
| T17, T16, D, D7, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | G1, G2, G3, G4, G5, 501, 502, 503, 504, 505 | ||||||
| SAT-1 APRON | |||||||
| RUNWAY | APRON | TAXI ROUTE DESIGNATOR | TAXI ROUTE DETAIL | AIRCRAFT STANDS | |||
| 01L | SAT-1 | SH5 / 01L | T18, H5, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | S115, S117, S119, S121, S123, S125, S127 | |||
| SH6 / 01L | T18, H6, H, D8, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | S101, S103, S105, S107, S109, S111, S113 | |||||
| SJ1 / 01L | T19, J1, J, D10, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | S116, S118, S120, S122, S124, S126, S128 | |||||
| SJ2 / 01L | T19, J2, J, D10, E TO HOLDING POSITION E21 | S102, S104, S106, S108, S110, S112, S114 | |||||
6. Runway Utilization Procedures
The runway-in-use is selected by Suvarnabhumi Control Tower as the best for general purpose. If it is unsuitable for a particular operation, the pilot can obtain permission from ATC to use another but must accept that he may thereby incur a delay.
| Friction Value | Determination of the value |
| >0.34 | Normal |
| ≤0.34 | (NOTAM will be promulgated) May be slippery when wet |
Departing aircraft will normally be directed by ATC to use the full length of the runway for take-off. Pilots-in-command may request or ATC may propose an intersection departure to resolve a particular runway or manoeuvring area conflict. The final decision whether to make an intersection departure rests with the pilot-in-command.
A pilot receiving an immediate take-off instruction is required to act as follows:
if waiting clear of the runway, taxi immediately on to it and begin his take off run without stopping his aircraft;
if already lined up on the runway, take off without delay;
if unable to comply with the instruction, inform ATC immediately.
| RUNWAY 19L | TORA (M) |
| B1 | 4 000 |
| B2 | 3 870 |
| RUNWAY 19R | TORA (M) |
| E1 | 3 700 |
| E2 | 3 590 |
| RUNWAY 01R | TORA (M) |
| B13 | 4 000 |
| B12 | 3 890 |
| RUNWAY 01L | TORA (M) |
| E21 | 3 700 |
| E19 | 3 590 |
| RUNWAY 19L | TORA (M) |
| B3 | 2 970 |
| RUNWAY 19R | TORA (M) |
| E5 | 2 780 |
| RUNWAY 01L | TORA (M) |
| E15 | 2 670 |
| RUNWAY 01R | TORA (M) |
| B11 | 2 780 |
Remarks: The aircraft take-off from these points shall be approved when traffic permitted in VMC only.
| RUNWAY 19L | DISTANCE TO TURN OFF (M) |
| B8 | 1640 |
| B10 | 2050 |
| B11 | 2560 |
| RUNWAY 19R | DISTANCE TO TURN OFF (M) |
| E9 | 1470 |
| E13 | 2050 |
| E15 | 2440 |
| RUNWAY 01R | DISTANCE TO TURN OFF (M) |
| B7 | 1770 |
| B5 | 2350 |
| B3 | 2740 |
| RUNWAY 01L | DISTANCE TO TURN OFF (M) |
| E12 | 1360 |
| E7 | 2050 |
| E5 | 2560 |
Remarks: Distance to turn off is the distance of the respective runway to turn-off intersection.
7. Low Visibility Operations
Runway 19L via B8, B10, B11,B12, B13
Runway 01R via B7, B5, B3, B2, B1
Runway 19R via E9, E13, E15, E17, E19, E21
Runway 01L via, E12, E7, E5, E2, E1
Pilots not able to comply with these requirements should notify ATC immediately.
Runway 19L : B1, B2
Runway 01R : B13, B12
Runway 19R : E1, E2
Runway 01L : E21, E19
Taxiway B1, B2, B3, B11, B12, B13
Taxiway E1, E2, E5, E15, E19, E21
Taxiway B5, B7, B8, B10
Taxiway E7, E9, E12, E13
8. Adverse Weather Condition & Procedures
Adverse Weather Condition Warning at Suvarnabhumi International airport : Adverse weather condition that causes thunderstorms and/or strong wind and even lightning may endanger airside operation to a large extent. Therefore, when it is predicted to occur, the effective warning system shall be deployed for airside workers and vehicle operators. The objective of this warning is to elaborate how the situations of each phase are and to alert all the airside personnel to work more carefully and safely in the airfield. Adverse Weather Condition Warning at Suvarnabhumi International airport can be defined into 3 levels;
Level 1 Thunderstorms Observations Reporting: The report is used when thunderstorms are detected within 50 KM from Aerodrome Reference Point (ARP) and their directions are heading Suvarnabhumi International airport.
Level 2 Thunderstorms and/or Strong Wind Warning: This warning is used when thunderstorms and/or strong wind are more than 25 KT within 16 KM from Aerodrome Reference Point (ARP) and their directions are towards or over Suvarnabhumi International airport.
Level 3 Lightning Warning: The warning is employed when thunderstorms are over Suvarnabhumi International airport and lightning characteristic is obviously detected.
Suvarnbhumi International airport will notify all concerned units by announcing “Thunderstorms Warning” when adverse weather condition level 1 takes place. The details how the announcement is made has already distributed to the operators concerned by means of official letter.
When the condition of adverse weather condition level 1 terminates, Suvarnabhumi International airport will announce “Thunderstorms Warning Terminated”.
Airlines, Ground Service Providers, and Airside Operator’s Procedures
When receive the adverse weather condition level 1;
Report the situation to their staff.
Operate with carefulness, be alert of the aircraft and vehicle’ safety and tightly secure all ground service equipments.
When thunderstorms and/or strong wind are more than 25 KT within 16 KM from Aerodrome Reference Point (ARP) and their direction are towards or over the aerodrome, Suvarnabhumi International airport will notify all concerned units by announcing “Thunderstorms and Strong Wind Warning”
And when receive the cancellation of adverse weather condition, Suvarnabhumi International airport will announce as “Thunderstorms and Strong Wind Warning Terminated”
Airlines, Ground Service providers, and Airside Operator’s Procedures
When receive the adverse weather condition level 2;
Report the situation to their staff.
Remove the stair from the aircraft and tie the gantry securely to the ground and also close the front part of stair.
Ensure aircraft parking brake is applied during on the parking stand.
Ensure aerobridge is parked on the assigned markings and close the front part of it.
Bond the aircraft ground receptacle.
Ensure that light aircraft are parked facing head wind and secured to the ground.
When thunderstorms are over Suvarnabhumi International airport and may likely cause lightning, Suvarnabhumi International airport will notify all concerned units by announcing “Lightning Warning” and instantly turn on the red warning light and siren.
And when receive the cancellation of adverse weather condition, turn off the red warning light and siren and announce as “Lightning Warning Terminated”.
Suvarnabhumi Air Traffic Control Center’s Procedures
When receive the adverse weather condition warning level 3 from Airside Operations Control Center (AOCC), keep monitoring the situation and inform Flight Operation of the airlines concerned about the adverse weather condition warning level 3 at Suvarnabhumi International airport and/or announce through Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS).
Airlines, Ground Service Providers, and Airside Operator’s Procedures
When receive the adverse weather condition level 3;
Restrain from operating and stay in the nearby buildings, or vehicles, or lightning shelters, or high mass light poles within 22.60 M, or under aircraft with ground receptacle bonded and monitor the weather conditions outside periodically.
Avoid contacting or staying near the aircraft without ground receptacle connected.
When receive the lightning warning while being outside the building, do not lie down on the floor. Do sit on feet together with knees up in order to least contact with the ground and decrease the overall body height which might induce electricity through the body from the lightning currents.
Refrain from refueling the aircraft.
Airlines informs ground service providers the adverse weather condition warning level 3 and recommend them the temporary suspension of ground operations and cease the communication with pilot.
Arrival Aircraft
Aircraft designated to park at parking bay with Visual Docking Guidance System: VDGS;
While the aircraft is approaching to the parking bay, the License Mechanic who is responsible for aircraft conveyance shall monitor the aircraft movement in order to make sure the moving aircraft is safe. This should be done while he/she is in the safe area.
When the aircraft reaches the parking bay and is in the right position of stand markings, the License Mechanic shall coordinate with pilots to apply parking brake and bond the aircraft’s nose gear and aircraft ground receptacle. Also, wait for the cancellation of adverse weather condition warning from Suvarnabhumi International airport. Then, the operations could be done as normal.
Aircraft arranged to park at parking bay without Visual Docking Guidance System: VDGS;
Airlines and ground service providers must provide the License Mechanic who is responsible for aircraft conveyance to perform as Marshaller leading the aircraft to its parking bay.
When the aircraft reaches the parking bay and is in the right position of stand markings, the License Mechanic shall coordinate with pilots to apply parking brake and bond the aircraft’s nose gear and aircraft ground receptacle. And also, wait for the cancellation of adverse weather condition warning from Suvarnabhumi International airport. Then, the operations should be done as normal.
Departure Aircraft
Departure aircraft operating at parking bay should be done as follows;
While the aircraft is being pushed back from parking bay and/or being on the taxilane ready to take off with all engines started, operate a normal procedures until they are completed and the aircraft has taken off.
In case the aircraft is being pushed back but the engine is not started yet. If the ground service providers consider bringing the aircraft back to its parking bay and wait for the cancellation of adverse weather condition warning from Suvarnabhumi International airport, airline or ground service providers must inform AOCC of that decision. This is because the airport is needed to rearrange the parking bay for another arriving aircraft.
For the aircraft in no.2 which arranged to park at the Contact Gate that has passenger loading bridges, while waiting for the adverse weather condition warning to be cancelled and airline or ground service provider considers that the aircraft bridge is needed again, inform the Airside Operations Control Center (AOCC) accordingly. Also, follow the procedures for facility request from Suvarnabhumi International airport properly.
Suspending the operations of airlines and/or ground service providers is conducted solely for the sake of safety of all operators which was mutually decided between airline members/ ground service providers and the airport operator. Therefore, in case of flight delays, airlines and ground service providers shall not claim any compensation from Suvarnabhumi International airport or concerned units.
9. Modes of Operation
Segregated Parallel Approaches / Departures (Mode 4) will be the standard operating mode for Suvarnabhumi International airport. There may be semi-mixed operations, i.e. one runway is used exclusively for departures, while the other runway is used for a mixture of approaches and departures; or, one runway is used exclusively for approaches while the other is used for a mixture of approaches and departures, there may also be mixed operations, i.e. simultaneous parallel approaches with departures interspersed on both runways (ICAO DOC 9643). Several types of parallel runway operations, which are described as operational models may be conducted in segregated parallel approaches and departures.
9.3 Operational models
The operational models applicable to Suvarnabhumi are described, together with related RNAV SIDs as follows.
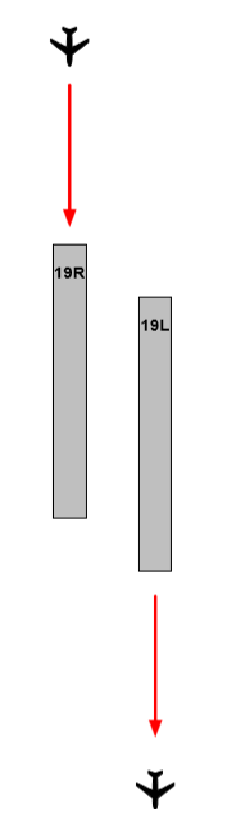
| MODEL 1 SEGREGATED PARALLEL OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
 | W1,A202 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | ANTIC 1C DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 19L | ANTIC 1C DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
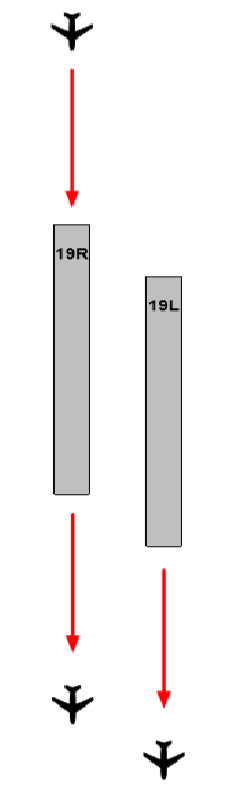
| MODEL 2 SEMI - MIXED OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
 | W1,A202 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 19R | COMET 1B DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
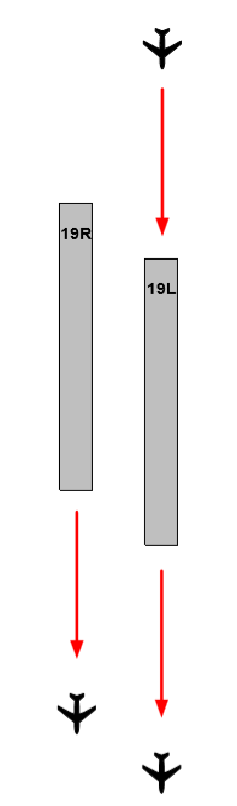
| MODEL 3 SEMI - MIXED OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
 | W1,A202 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 19R | COMET 1B DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
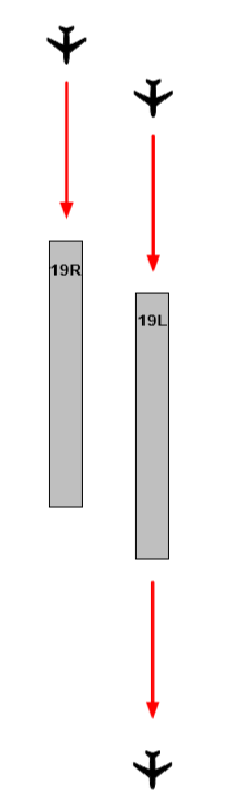
| MODEL 4 SEMI - MIXED OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
 | W1, A202 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | ANTIC 1C DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 19L | ANTIC 1C DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 19L | NESTA 1C DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
| MODEL 5 SEMI - MIXED OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
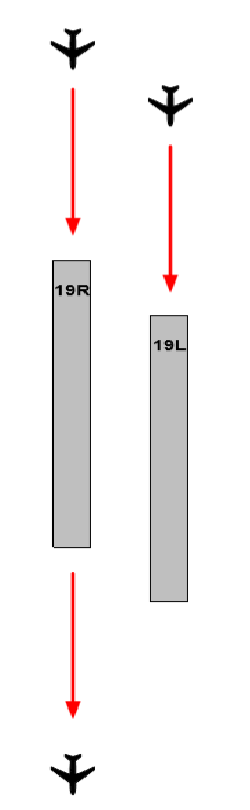 | W1, A202 | 19R | COSMO 1 B DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 19R | COSMO 1B DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 19R | COSMO 1B DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19R | COSMO 1B DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 19R | SIMON 1B DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 19R | SIMON 1B DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 19R | COMET 1B DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 19R | COMET 1B DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
| MODEL 6 MIXED OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
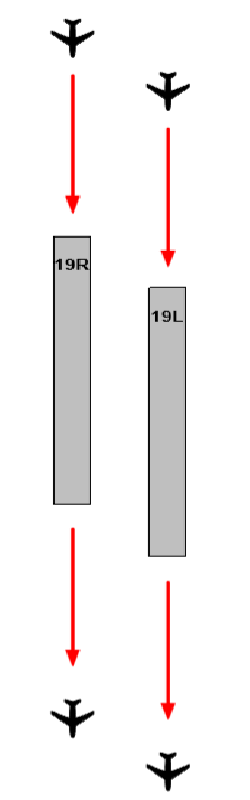 | W1, A202 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19L | COSMO 1C DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 19L | SIMON 1C DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 19L | SEESA 1C DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 19R | COMET 1B DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 19R | ANTIC 1B DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 19R | NESTA 1B DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
| MODEL 7 SEGREGATED PARALLEL OPERATION | ||||
|
OPERATIONAL CONDITIONS
| ||||
| FIGURE | AIRWAYS | DEPARTURE RUNWAY | RNAV SIDs | |
 | W1, A202 | 01L | CHEST 1B DEPARTURE KRT TRANSITION | |
| A1 | 01L | CHEST 1B DEPARTURE SELKA TRANSITION | ||
| G474 | 01L | CHEST 1B DEPARTURE BATOK TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 01L | CHEST 1B DEPARTURE GOMES TRANSITION | ||
| N891 | 01L | CHEST 1B DEPARTURE RYN TRANSITION | ||
| R201 | 01L | FIRNN 1B DEPARTURE BUT TRANSITION | ||
| A464, M751, W19 | 01L | FIRNN 1B DEPARTURE REGOS TRANSITION | ||
| G458, W31 | 01L | FIRNN 1B DEPARTURE HOTEL TRANSITION | ||
| R468 | 01L | JEANS 1B DEPARTURE TANEK TRANSITION | ||
| G463, P646 | 01L | JEANS 1B DEPARTURE BETNO TRANSITION | ||
| A1, L507 | 01L | JEANS 1B DEPARTURE LIMLA TRANSITION | ||
| A464 | 01L | JEANS 1B DEPARTURE BEKOD TRANSITION | ||
| W9 | 01L | JEANS 1B DEPARTURE TL TRANSITION | ||
| B346, W21 | 01L | JORGE 1B DEPARTURE NOBER TRANSITION | ||
| R474 | 01L | JORGE 1B DEPARTURE ALBOS TRANSITION | ||
10. Removal of disabled aircraft.
11. Hot Spot (HS) Areas.
12. Starting and Running of Aircraft Engine Procedures.
12.2 Run-Up of Aircraft Engines
13. VISUAL DOCKING GUIDANCE SYSTEM
B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6
C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, C7, C8, C9, C10
D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8
E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, E7, E8, E9, E10
F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6
G1, G2, G3, G4, G5
115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125, 126, 127, 128, 129
201, 202, 203
301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 308
401, 402, 403
501, 502, 503, 504, 505, 506, 507, 508, 509, 510, 511, 512, 513, 514, 515, 516, 517, 518, 519, 520, 521, 522, 523, 524, 525
Description of system see VTBS AD 2.20 item 13.2.1
Description of system see VTBS AD 2.20 item 13.2.2
S113R, S114L, S114, S114R, S115L, S115, S115R, S116L, S116, S116R, S117L, S117, S117R, S118L, S118, S118R
S119, S120, S121, S122, S123, S124, S125, S126, S127, S128
Description of system see VTBS AD 2.20 item 13.2.3
E1-E10, F1-F6, G1-G5, 115-129, 201-203, 301-308, 401-403 and 501-525.
The RLG GIS206-2 Laser Guided Docking System is a fully automatic aircraft docking guidance system for various types of modern aircraft.
The system utilizes 2-axis laser scanning technique to track both the lateral and longitudinal positions of the incoming aircraft and guide the aircraft to the programmed stopping position. In addition, the system also has aircraft ID verification feature to identify the incoming aircraft and check it against the one selected by the operator. If the incoming aircraft fails to match the expected aircraft, an ‘ID FAIL’ indication is immediately issued via display information console to both the pilot and the co-pilot.
Aircraft type, continuous closing distance, and azimuth guidance, etc., are presented on a single console clearly visible to both the pilot and co-pilot, simultaneously. Figure A shows the Aircraft Display console, mounted on the terminal in front of the aircraft stand.
The system is operated only in the automatic mode. If the system fails, the aircraft must then be marshalled into the stand manually.
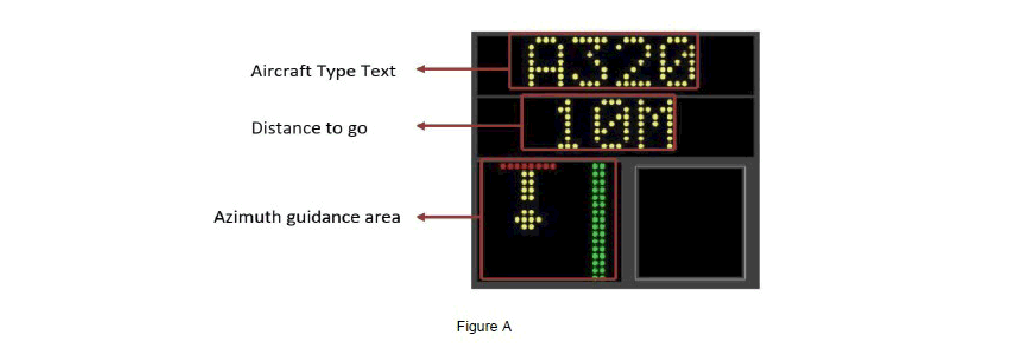
Pilot must stop the aircraft immediately if he or she sees that:
The docking system is not activated.
A wrong aircraft type is display.
The word STOP is displayed.
A wrong type of aircraft indicates ‘ID FAIL’ is displayed.
Passenger loading bridges will be activated in the range as follows:
between 0.01-1.50 M are normally serviceable.
between 1.51 – 2.00 M, passenger loading bridge (PLB) called “L1” is only serviceable, if the PLB called “L2” is required,
the aircraft shall push back to correct stop-position.the distance over 2.00 M, passenger loading bridges are unserviceable, if required the aircraft shall pushed back to correct stop-position.
Any overshoot distance is made by A380, push back to correct stop position is needed when passenger loading bridges are required.
Remark: The identification of passenger loading bridge (L1 or L2) is followed by aircraft door positions.
13.2.1.1.3 Emergency Stop Button information
Emergency stop buttons are available at both of contact gates and remote parking stand. When unsafe situation is considered, the emergency stop button shall be pressed by bridge driver, marshaller or the ground engineer of the airline or handling agent. Emergency stop buttons are installed in the locations as follows:
At the control panel in the bridge cab
At the bridge rotunda
At the stand identification posts
13.2.1.2 Docking Procedure
The pilot display of the Advanced Visual Docking Guidance System (A-VDGS) is shown below:
PARKING SEQUENCE:
 | In this picture the aircraft is at a distance greater than Note that the progress bar and digital close-in distance are not displayed when the aircraft is greater than Airbus 320 aircraft is expected. |
 | In this picture the aircraft is at exactly 30 metres from Starting at 30 metres, the digital close-in distance (second line of display) is displayed, in 1 metre decrements. The progress meter (lower left) will also be activated at this distance. |
 | The aircraft is at 20 metres from the docking position and has returned to the centre line. Note the position of progress meter. The arrow will advance one position every 2.5 metres. |
 | In this picture the aircraft is at 10 metres and is on |
 | The aircraft is now at 3.2 metres from the stop position and is on the centre line. Note that at below 5 metres, the close-in distance is displayed in 0.2 M decrements. |
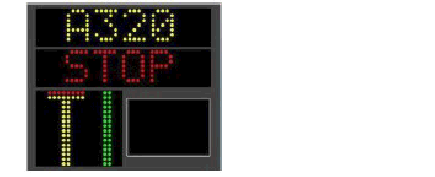 | Finally the aircraft is perfectly parked at the stop position, and perfectly centred. The word “STOP” is displayed in red. Note also the merging of the arrow and the stop line |
 | The word “OK” is displayed in yellow. Docking is successful. |
SLOW:
| During the docking process, the pilot must taxi into the aircraft stand at minimum speed. The system will display “SLOW” alternating SLOW message if the system detects the aircraft taxi speed is beyond the range of the preset speed and causing too fast for reliable detection. The “SLOW” message will return to close-in distance information once the aircraft speed is back to normal speed range. |
ID FAIL:
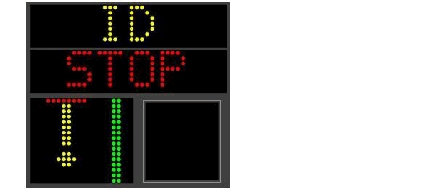  | For this aircraft type ID verification features, the incoming aircraft must be identified and verified at least 12 metres before the stopping position or otherwise, the system will display “ID FAIL” alternating ID/FAIL in the first row of the display. The second row of the docking screen will indicate “STOP”. At this point, the aircraft must be manually guided in by a marshaller. |
TOO FAR:
 | If the aircraft overshoots the preset range, the word “TooFar” will be displayed. The second row of the docking screen will indicate “STOP”. The aircraft shall stop immediately. |
ERROR STOP:
 | The system will display “Error” message as indicated if the system detects any hardware error that might affect the normal docking process. The second row of the display will indicate “STOP”and no aircraft is to be allowed to march in untilthe maintenance personnel has rectified the issue. |
EMERGENCY STOP:
 | The first and second row of the display will show “STOP”. The docking is aborted and aircraft must be manually guided in by a marshaller. |
The VDGS System has built in error detection program to inform the aircraft pilot of impending dangers during the docking procedure.
Warning: If the pilot is unsure of the information, being shown on the VDGS display unit, he must immediately stop the aircraft and obtain further information for clearance.
Warning: The pilot shall not enter the stand area unless the docking system first is showing the vertical running arrows. The pilot must not proceed beyond the bridge unless these arrows have been superseded by the closing rate bar.
Warning: The pilot shall not enter the stand area unless the aircraft type displayed is equal to the approaching aircraft. The correctness of other information, such as “Door 2” shall also be checked.
The message STOP SBU means that docking has been interrupted and has to be resumed only by manual guidance.
Warning: DO NOT TRY TO RESUME DOCKING WITHOUT MANUAL GUIDANCE.
Passenger loading bridges will be activated in the range as follows:
between 0.01-1.50 M are normally serviceable.
between 1.51 – 2.00 M, passenger loading bridge (PLB) called “L1” is only serviceable, if the PLB called “L2” is required, the aircraft shall push back to correct stop-position.
the distance over 2.00 M, passenger loading bridges are unserviceable, if required the aircraft shall pushed back to correct stop-position.
Any overshoot distance is made by A380, push back to correct stop position is needed when passenger loading bridges are required.
Remark: The identification of passenger loading bridge (L1 or L2) is followed by aircraft door positions.
Emergency stop buttons are available at both of contact gates and remote parking stand. When unsafe situation is considered, the emergency stop button shall be pressed by bridge driver, marshaller or the ground engineer of the airline or handling agent. Emergency stop buttons are installed in the locations as follows:
At the control panel in the bridge cab
At the bridge rotunda
At the stand identification posts
13.2.2.2 Docking Procedure
START-OF-DOCKING
 | Pressing one of the aircraft type buttons on the Operator Panel starts the system. When the button has been pressed,WAIT will be displayed. |
CAPTURE
 | The floating arrows indicate that the system is activated and in capture mode, searching for an approaching aircraft. |
TRACKING
 | When the laser has caught the aircraft, the floating arrowsare replaced by the yellow centre line indicator. |
CLOSING RATE
 | Display of digital countdown will start when the aircraft is20 M from stop position. This information is shown insteadof the flight number. |
ALIGNED TO CENTRE
 | The aircraft is 8 metres from the stop position. |
SLOW DOWN
 | If the aircraft is approaching faster than the accepted speed, the system will show SLOW DOWN as a warning to the pilot. |
AZIMUTH GUIDANCE
 | The yellow arrow indicates an aircraft to the right ofthe centre line and the red flashing arrow indicatesthe direction to turn. The aircraft is 4 M from the stop position in this example. |
STOP POSITION REACHED
 | When the correct stop position is reached, the displaywill show STOP and red lights will be lit. |
DOCKING COMPLETED
 | When the aircraft has parked, OK will be displayed. |
OVERSHOOT
 | If the aircraft has overshoot the stop position, TOO FARwill be displayed. |
STOP SHORT
 | If the aircraft is found standing still but has not reached Also the red lights are lit. |
WAIT
 | If the detected aircraft is lost during docking, before 12 Mto STOP, the display will show WAIT. The docking willcontinue as soon as the system detects the aircraft againand the closing-rate bar is shown. The pilot must not proceed beyond the bridge unless the “WAIT” message has been superseded by the closing rate bar. |
BAD WEATHER CONDITION
 | During heavy fog, rain or snow, the visibility for the dockingsystem can be reduced. When the system is activated and in capture mode, and a downgrade condition is detected, the pilot display will start flashing the Aircraft Type, show a DOWN GRADE message and replace the rolling arrows with a blank The blank lead-in display will be replaced with the normallead-in bar, once Safedock has been able to acquire a lockonto the aircraft. The DOWN GRADE messageand the flashing aircraft type will remain in the displaythroughout the docking procedure. The pilot must not proceed beyond the bridge unless the closing rate bar is shown. |
AIRCRAFT VERIFICATION FAILURE
 | During entry into the stand, the aircraft geometry is beingchecked. If, for any reason, aircraft verification is not made12 M before the stop position, the display will first showWAIT and make a second verification check. If this failsSTOP and ID FAIL will be displayed. The text will bealternating on the upper two rows of the display. The pilot must not proceed beyond the bridge unless the WAIT message has been superseded by the closing rate bar. |
GATE BLOCKED
 | If an object is found blocking the view from the VDGSto the planned stop position for the aircraft, the dockingprocedure will be halted with a wait and GATE BLOCKmessage. The docking procedure will resume as soon asthe blocking object has been removed. The pilot must not proceed beyond the bridge unless the WAIT message has been superseded by the closing rate bar. |
VIEW BLOCKED
 | If the view towards the approaching aircraft is hinderedfor instance by dirt on the window, the VDGS will reporta View block condition. Once the system is able to seethe aircraft through the dirt, the message will be replacedwith a closing rate display. The pilot must not proceed beyond the bridgeunless the WAIT message has been superseded bythe closing rate bar. |
SBU-STOP
 | Any unrecoverable error during the docking procedurewill generate an SBU (safety backup) condition.The display will show red stop bar and the text STOP SBU. A manual backup procedure must be used for dockingguidance. |
TOO FAST
 | If the aircraft approaches with a speed higher thanthe docking system can handle, the message STOP(with red squares) and TOO FAST will be displayed. The docking system must be re-started or the dockingprocedure completed by manual guidance. |
EMERGENCY STOP
 | When the Emergency Stop button is pressed,STOP is displayed with red squares. |
CHOCK ON
 | CHOCK ON will be displayed, when the ground staff has put the chocks in front of the nose wheel and pressed the “Chocks On” button on the Operator Panel. |
ERROR
 | If a system error occurs, the message ERROR is displaywith an error code. The code is used for maintenancepurposes and explained elsewhere. |
SYSTEM BREAKDOWN
 | In case of a severe system failure, the display will go black except for a red stop indicator. A manual backup |
POWER FAILURE
 | In case of a power failure, the display will be completelyblack. A manual backup procedure must be used fordocking guidance. |


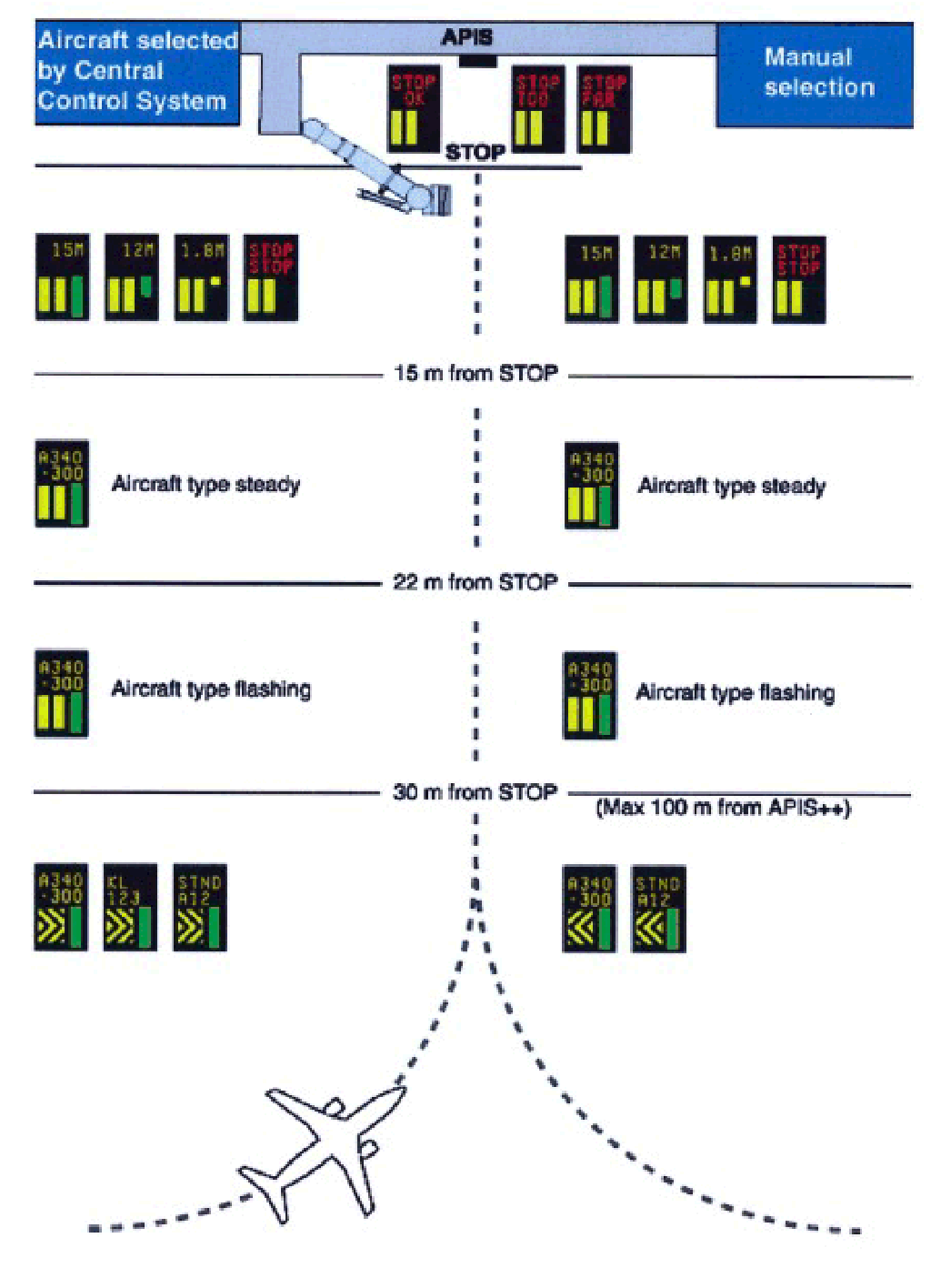
System detections
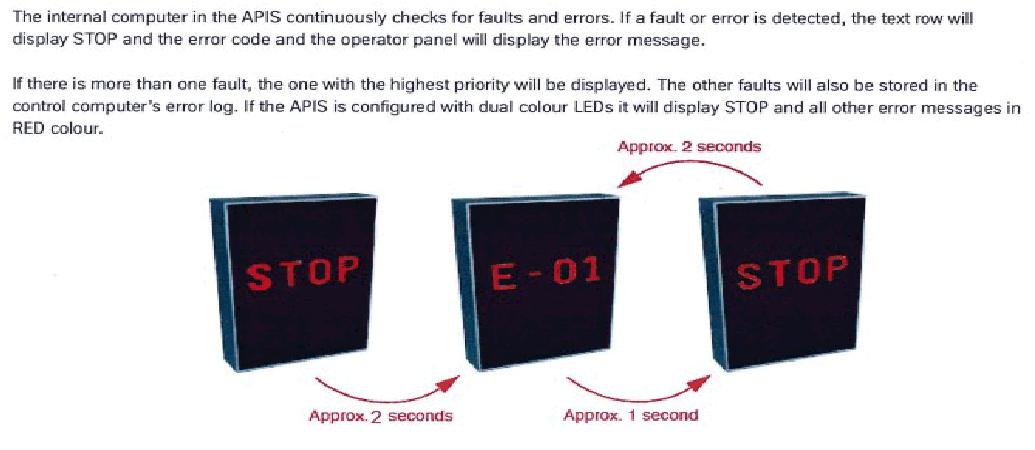
Continuous check during docking

Bridge in stop

Emergency stop

Too Far

VTBS AD 2.21 NOISE ABATEMENT PROCEDURES
1. NOISE ABATEMENT PROCEDURES AT SUVARNABHUMI INTERNATIONAL AIRPORT DETAIL AS FOLLOW:
All departing aircraft are required to apply noise abatement procedure with thrust reduction at 1 500 FT AGL, And acceleration at 3 000 FT AGL.
VTBS AD 2.22 FLIGHT PROCEDURES
1. Provision of Radar Services
2. Approach Procedures with Radar Control
3. Standard Instrument Departures/Arrivals (RNAV SIDs/STARs)
Aircraft departing from or arriving at Suvarnabhumi International Airport will normally be assigned the RNAV SIDs /STARs detailed in VTBS AD 2.24.
Note: Pilots of Non-RNAV equipped aircraft shall inform ATC and request for radar vectors.
4. Speed Control and Altitude Restrictions Promulgation in Bangkok TMA
In order to facilitate the air traffic flow procedure of departing and arriving aircraft within Bangkok TMA, speed control procedures and altitude restricted must be applied to optimize the spacing between aircraft and reduce the overall delay of traffic.
When a departing aircraft on a SID is cleared to climb to a level higher than the initially cleared level or the level(s) specified in the SID, the aircraft shall nevertheless follow the published vertical profile, unless such restrictions are explicitly cancelled by ATC.
5. TCAS RA Warning
Avoidance of unnecessary TCAS RA warning, aircraft shall strictly use rate of climb or rate of descent at 1500 FPM or less within 2000 FT to the assigned altitude or flight level, then use rate of climb or rate of descend at 1000 FPM or less within 1000 FT to the assigned altitude or flight level when flight crew is made aware of another aircraft at or approaching an adjacent altitude or flight level, unless otherwise instructed by ATC.
6. Operational for safety and more effective Air Traffic Management in Bangkok TMA.
Suvarnabhumi Departure shall be established to provide Air Traffic Control Service at Suvarnabhumi International airport, the operational procedures shall be as follows:
7. Reduce communication workload
8. Delay during severe weather
4 minutes or more between successive departures on the same SID or between aircraft intending to fly in the direction where severe weather is reported
4 minutes or more between successive arrivals on the same STAR/at the same IAWP or between aircraft intending to fly in the direction where severe weather is reported
9. VFR Flights at VTBS
A pilot wishing to conduct special VFR flight is to call Bangkok Approach on frequency 125.8 MHz for special VFR clearance.
The details of VFR entry and exit procedures are given in ENR 2.2, Item 1. VFR ENTRY AND EXIT PROCEDURES IN BANGKOK CONTROL ZONE.
Aircraft will not be permitted to take off unless two-way radio communications can be maintained with the control tower.
Report their position, distance, heading and altitude as well as departure point when approaching 50 NM from BKK VOR by blind transmission.
Observe the direction of traffic in pattern and enter downwind with the flow of traffic.
Conform to the altitude for the type of aircraft as listed in Note below.
Make a low approach along the runways at an altitude of 500 FT, and rock the wings of the aircraft.
Re-enter downwind leg and observe light signals.
Note: Traffic Patterns and Altitudes:
Jet aircraft 1500 FT
Light aircraft 1000 FT
Helicopter 500 FT
Traffic Pattern is shown below:
Illustration of Traffic Pattern
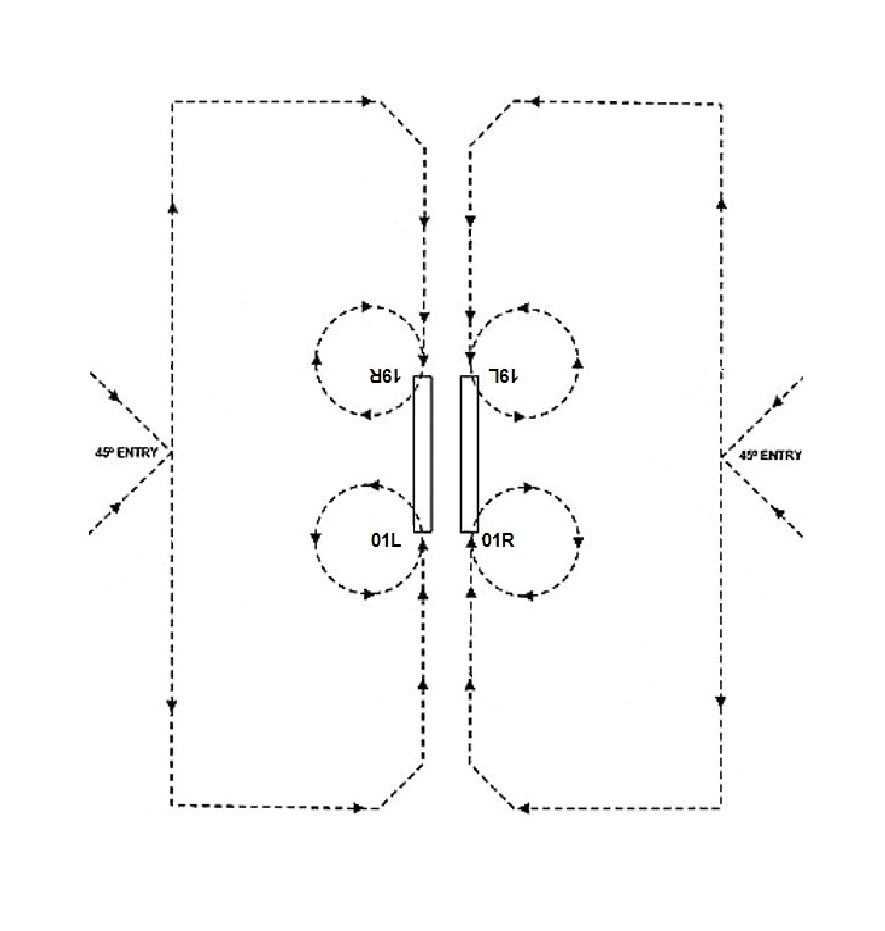
10. ATC Clearance Procedures
| Frequency | Outbound routes |
|---|---|
| 128.7 MHZ | A464 (Northbound), A464 (Southbound), B346, G458, G463, L301, L507, M502, M751, M757, P646, R474, W9, W19, W21, W31, Y6, Y8 |
| 133.8 MHZ | A1, G474, M904, N891, R201, R468, Y11, Y16 |
Remark: IFR aircraft departing to VTBD, VTBU, VTBK, VTBL, VTPI and VTPH at or below FL160 are to call Bangkok Approach on 125.8 MHz
Call sign
Type of aircraft
Destination
Route
Proposed flight level, if different from the filed flight plan and,
When applicable, special requirements (e.g. inability to comply with SID climb profile).
Under normal circumstances, altitude 6000 FT shall be initially assigned.
First airborne first flight level selection principle.
No one ground flight level negotiation and reservations.
Cruising level shall be assigned by Bangkok Control after airborne.
Keep listening watch on relevant Suvarnabhumi Ground Control frequency at all times for additional or revised ATC clearance and in readiness for push back; and
Call Ground Control in the appropriate time with the departure time restriction.
11. Fuel Dumping Procedure and In-flight Management Procedures
An aircraft in emergency or other urgent situations may need to dump fuel so as to reduce to maximum landing mass in order to affect a safe landing.
Illustration of Fuel dumping areas
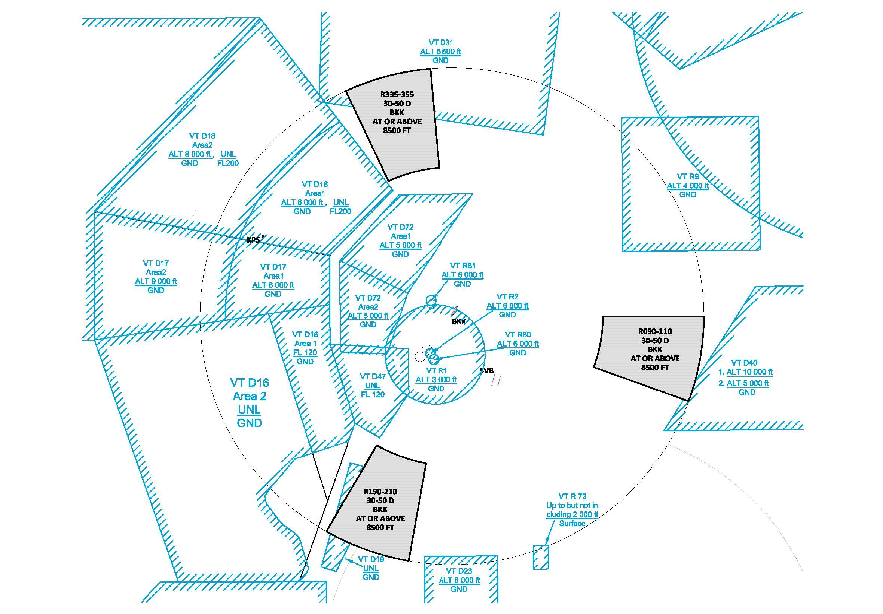
Minimum fuel: The term used to describe a situation in which an aircraft’s fuel supply has reached a state where the flight is committed to land at a specific aerodrome and no additional delay can be accepted.
Mayday fuel: Describes the nature of the distress conditions when the calculated usable fuel predicted to be available upon landing at the nearest aerodrome where a safe landing can be made is less than the planned final reserve fuel
Note 1: The declaration of “MINIMUM FUEL” informs ATC that all planned aerodrome options have been reduced to a specific aerodrome of intended landing and any changes to the existing clearance may result in landing with less than planned final reserve fuel. This is not an emergency situation but an indication that an emergency situation is possible should any additional delays occur.
Note 2: It should be noted that Pilots should not expect any form of priority handling as a result of a “MINIMUM FUEL” declaration. ATC will, however, advise the flight crew of any additional expected delays as well as coordinate when transferring control of the aircraft to ensure that other ATC units are aware of the flight’s fuel state.
Note 1: The planned final reserve fuel refers to the value calculated in Annex 6 - Operation of Aircraft, Chapter4, item 4.3.6.3 e) 1) or 2) and is the minimum amount of fuel required upon landing at any aerodrome.
Note 2: The words “MAYDAY FUEL” describe the nature of the distress conditions as required in Annex 10, Volume II, Chapter 5, Item 5.3.2.1, b) 3).
Note 3: Guidance on procedures for in-flight fuel management is contained in the Fuel Planning Manual (Doc 9976).
The estimated delay, if pilots are en-route to, joining or are established in holding point such as IAWPs; or
The estimated track mileage, if pilots are being vectored to an instrument approach; or
Pilot transmission: (C/S), MINIMUM FUEL
Controller transmission: (C/S), ROGER [NO DELAY EXPECTED or EXPECT (delay information)]
Pilot Transmission: (C/S) MAYDAY, MAYDAY, MAYDAY FUEL
Controller transmission: (C/S) ROGER MAYDAY
12. Aircraft Transponder Failure Procedures
Phraseologies
“C/S, CONFIRM TRANSPONDER ON”, or
“C/S, CHECK YOUR TRANSPONDER OPERATED NORMALLY”, or
“C/S, TRANSPONDER NOT RECEIVED, CHECK FUNCTIONALITY”
When it has been confirmed that aircraft transponder fails, ATC shall advice the pilot to repair it before departure. However, the surface radar blind spot, where the transponder might not be easily detected, should be taken into consideration.
Phraseologies
“C/S, ADVISE TRANSPONDER REPAIRED BEFORE DEPARTURE”, or
“C/S, ADVISE RETURN TO BAY FOR TRANSPONDER REPAIRING”
Phraseologies
“C/S, CONFIRM TRANSPONDER ON”, or
“C/S, CHECK YOUR TRANSPONDER OPERATED NORMALLY”, or
“C/S, TRANSPONDER NOT RECEIVED, CHECK FUNCTIONALITY”
When it has been confirmed that the aircraft transponder fails, ATC shall advice the pilot to return to his departure airport as well as relay all necessary information to Aerodrome Control Tower and all concerned units.
Phraseologies
“C/S, ADVISE RETURN TO LAND AT (DEPARTURE AERODROME) FOR TRANSPONDER REPAIRING, REQUEST YOUR INTENTION”,
“C/S, ADVISE RETURN TO BAY FOR TRANSPONDER REPAIRING”
In case pilot decide to proceed to first intended landing or nearest suitable aerodrome, primary radar separation shall be provided. However, the pilot shall be reminded that delays can be expected and some requests might not be granted e.g. route to be flown, cruising altitude/level.
12.2.1 ATC must immediately inform the pilot of his transponder failure so that he could check its operations and repair it.
13. Radio communication failure procedure
Proceed according to the STAR route to the termination point (WALTZ/EKCHO for RWY 19L/R or WOCAL/ENKAA for RWY 01L/R) and descend in accordance with the published all speed and altitude restrictions of the relevant STAR procedure, thence:
For RWY 19L/R: After passing WALTZ/EKCHO, the pilot shall fly heading 015 and maintain altitude 6 000 FT for next 10 NM, then turn right/left and descend to 2 000 FT and carry out the appropriate ILS approach procedure.
For RWY 01L/R: After passing WOCAL/ENKAA, the pilot shall fly heading 195 and maintain altitude 6 000 FT for next 10 NM, then turn right/left and descend to 2 000 FT and carry out the appropriate ILS approach procedure.
Pilots may endeavour to communicate with ATC by telephone network.
The telephone numbers are as follows:
Don Mueang Tower Tel: +662 515 3282, +662 515 3288, +6681710 7449
Suvarnabhumi Tower Tel: +662 131 3610-3, +6686 399 9030
Bangkok Approach Tel: +662 131 3621, +662131 2622, +6685 150 2288 and +6685 150 3300
VTBS AD 2.23 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
1. Bird concentrations
Wildlife Hazard Control staff
Phone +662 132 6981, +662 132 6982
E-mail: [email protected]
Highly endangered kinds are as follows:
| Species | Weight (KG) | Period |
|---|---|---|
| Open-billed stork | 2.3 - 4.4 | All year (mostly in June - July) |
| Painted stork | 2 - 3 | All year (mostly in June - July) |
| Cattle Egret | 0.3 - 0.4 | All year (mostly in July - November) |
| Oriental Pratincole | 0.07 - 0.095 | February - November |
| Black-winged Stilt | 0.25 - 0.3 | All year (mostly in April - February) |
| Red Collared Dove | 0.08 - 0.1 | All year (mostly in June - October) |
Remark: Bird concentrations chart is shown in page AD2-VTBS-9-1 Dated 18 July 2019
grass areas outside the boundary of runways strip and the critical area.
grass areas outside the boundary of taxiways strip. For safety reason, the work will temporary stop when taxiing aircraft approaches.
VTBS AD 2.24 CHARTS RELATED TO AN AERODROME
|
Chart name |
Page |
|---|---|
|
Aerodrome/Heliport Chart - ICAO | AD 2-VTBS-2-1 |
|
Aircraft Parking/Docking Chart - ICAO | AD 2-VTBS-2-3 |
|
Aircraft Parking/Docking Chart - ICAO (Verso 1) | AD 2-VTBS-2-4 |
|
Aircraft Parking/Docking Chart - ICAO (Verso 2) | AD 2-VTBS-2-5 |
|
Aircraft Parking/Docking Chart - ICAO (Verso 3) | AD 2-VTBS-2-6 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Inbound - Landing RWY 19R | AD 2-VTBS-2-7 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Inbound - Landing RWY 19L | AD 2-VTBS-2-9 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Inbound - Landing RWY 01R | AD 2-VTBS-2-11 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Inbound - Landing RWY 01L | AD 2-VTBS-2-13 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Outbound - Take-off RWY 19R | AD 2-VTBS-2-15 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Outbound - Take-off RWY 19L | AD 2-VTBS-2-17 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Outbound - Take-off RWY 01R | AD 2-VTBS-2-19 |
|
Aerodrome Ground Movement Chart - ICAO - Standard Taxi Route - Outbound - Take-off RWY 01L | AD 2-VTBS-2-21 |
|
Aerodrome Obstacle Chart - ICAO - Type A - RWY 01L/19R | AD 2-VTBS-3-1 |
|
Aerodrome Obstacle Chart - ICAO - Type A - RWY 01R/19L | AD 2-VTBS-3-3 |
|
Precision Approach Terrain Chart - ICAO - RWY 01L/19R | AD 2-VTBS-3-5 |
|
Precision Approach Terrain Chart - ICAO - RWY 01R/19L | AD 2-VTBS-3-7 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J | AD 2-VTBS-6-1 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-2 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-3 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-4 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-5 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J (Tabular description 4) | AD 2-VTBS-6-6 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - ALBOS3J BONVO3J NOBER3J NUNLI3J PASTO3J ROBKA3J SEMBO3J TANGO3J TARED3J TL3J UPKUP3J (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-7 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - DOSBU3J GORSI3J HHN3J KASNI3J KIGOB3J REGOS3J RYN3J SABIS3J UKERA3J | AD 2-VTBS-6-9 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - DOSBU3J GORSI3J HHN3J KASNI3J KIGOB3J REGOS3J RYN3J SABIS3J UKERA3J (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-10 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - DOSBU3J GORSI3J HHN3J KASNI3J KIGOB3J REGOS3J RYN3J SABIS3J UKERA3J (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-11 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - DOSBU3J GORSI3J HHN3J KASNI3J KIGOB3J REGOS3J RYN3J SABIS3J UKERA3J (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-12 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - DOSBU3J GORSI3J HHN3J KASNI3J KIGOB3J REGOS3J RYN3J SABIS3J UKERA3J (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-13 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L - DOSBU3J GORSI3J HHN3J KASNI3J KIGOB3J REGOS3J RYN3J SABIS3J UKERA3J (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-14 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G | AD 2-VTBS-6-15 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-16 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-17 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-18 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-19 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G (Tabular description 4) | AD 2-VTBS-6-20 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - ALBOS3G BONVO3G NOBER3G NUNLI3G PASTO3G ROBKA3G SEMBO3G TANGO3G TARED3G TL3G UPKUP3G (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-21 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - DOSBU3G GORSI3G HHN3G KASNI3G KIGOB3G REGOS3G RYN3G SABIS3G UKERA3G | AD 2-VTBS-6-23 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - DOSBU3G GORSI3G HHN3G KASNI3G KIGOB3G REGOS3G RYN3G SABIS3G UKERA3G (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-24 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - DOSBU3G GORSI3G HHN3G KASNI3G KIGOB3G REGOS3G RYN3G SABIS3G UKERA3G (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-25 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - DOSBU3G GORSI3G HHN3G KASNI3G KIGOB3G REGOS3G RYN3G SABIS3G UKERA3G (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-26 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - DOSBU3G GORSI3G HHN3G KASNI3G KIGOB3G REGOS3G RYN3G SABIS3G UKERA3G (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-27 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19R - DOSBU3G GORSI3G HHN3G KASNI3G KIGOB3G REGOS3G RYN3G SABIS3G UKERA3G (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-28 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - ALBOS3H BONVO3H NOBER3H NUNLI3H PASTO3H ROBKA3H SEMBO3H TANGO3H TARED3H TL3H UPKUP3H | AD 2-VTBS-6-29 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - ALBOS3H BONVO3H NOBER3H NUNLI3H PASTO3H ROBKA3H SEMBO3H TANGO3H TARED3H TL3H UPKUP3H (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-30 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - ALBOS3H BONVO3H NOBER3H NUNLI3H PASTO3H ROBKA3H SEMBO3H TANGO3H TARED3H TL3H UPKUP3H (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-31 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - ALBOS3H BONVO3H NOBER3H NUNLI3H PASTO3H ROBKA3H SEMBO3H TANGO3H TARED3H TL3H UPKUP3H (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-32 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - ALBOS3H BONVO3H NOBER3H NUNLI3H PASTO3H ROBKA3H SEMBO3H TANGO3H TARED3H TL3H UPKUP3H (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-33 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - ALBOS3H BONVO3H NOBER3H NUNLI3H PASTO3H ROBKA3H SEMBO3H TANGO3H TARED3H TL3H UPKUP3H (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-34 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - DOSBU3H GORSI3H HHN3H KASNI3H KIGOB3H REGOS3H RYN3H SABIS3H UKERA3H | AD 2-VTBS-6-35 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - DOSBU3H GORSI3H HHN3H KASNI3H KIGOB3H REGOS3H RYN3H SABIS3H UKERA3H (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-36 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - DOSBU3H GORSI3H HHN3H KASNI3H KIGOB3H REGOS3H RYN3H SABIS3H UKERA3H (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-37 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - DOSBU3H GORSI3H HHN3H KASNI3H KIGOB3H REGOS3H RYN3H SABIS3H UKERA3H (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-38 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - DOSBU3H GORSI3H HHN3H KASNI3H KIGOB3H REGOS3H RYN3H SABIS3H UKERA3H (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-39 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L - DOSBU3H GORSI3H HHN3H KASNI3H KIGOB3H REGOS3H RYN3H SABIS3H UKERA3H (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-40 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - ALBOS3K BONVO3K NOBER3K NUNLI3K PASTO3K ROBKA3K SEMBO3K TANGO3K TARED3K TL3K UPKUP3K | AD 2-VTBS-6-41 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - ALBOS3K BONVO3K NOBER3K NUNLI3K PASTO3K ROBKA3K SEMBO3K TANGO3K TARED3K TL3K UPKUP3K (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-42 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - ALBOS3K BONVO3K NOBER3K NUNLI3K PASTO3K ROBKA3K SEMBO3K TANGO3K TARED3K TL3K UPKUP3K (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-43 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - ALBOS3K BONVO3K NOBER3K NUNLI3K PASTO3K ROBKA3K SEMBO3K TANGO3K TARED3K TL3K UPKUP3K (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-44 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - ALBOS3K BONVO3K NOBER3K NUNLI3K PASTO3K ROBKA3K SEMBO3K TANGO3K TARED3K TL3K UPKUP3K (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-45 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - ALBOS3K BONVO3K NOBER3K NUNLI3K PASTO3K ROBKA3K SEMBO3K TANGO3K TARED3K TL3K UPKUP3K (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-46 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - DOSBU3K GORSI3K HHN3K KASNI3K KIGOB3K REGOS3K RYN3K SABIS3K UKERA3K | AD 2-VTBS-6-47 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - DOSBU3K GORSI3K HHN3K KASNI3K KIGOB3K REGOS3K RYN3K SABIS3K UKERA3K (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-48 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - DOSBU3K GORSI3K HHN3K KASNI3K KIGOB3K REGOS3K RYN3K SABIS3K UKERA3K (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-6-49 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - DOSBU3K GORSI3K HHN3K KASNI3K KIGOB3K REGOS3K RYN3K SABIS3K UKERA3K (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-6-50 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - DOSBU3K GORSI3K HHN3K KASNI3K KIGOB3K REGOS3K RYN3K SABIS3K UKERA3K (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-6-51 |
|
Standard Departure Chart - Instrument (SID) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01R - DOSBU3K GORSI3K HHN3K KASNI3K KIGOB3K REGOS3K RYN3K SABIS3K UKERA3K (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-6-52 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C | AD 2-VTBS-7-1 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-7-2 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-7-3 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-7-4 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-7-5 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Tabular description 4) | AD 2-VTBS-7-6 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Tabular description 5) | AD 2-VTBS-7-7 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 19L/19R - DOLNI3C EASTE3C LEBIM3C NORTA3C WILLA3C (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-7-8 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D | AD 2-VTBS-7-9 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Radio communication failure table) | AD 2-VTBS-7-10 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Tabular description 1) | AD 2-VTBS-7-11 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Tabular description 2) | AD 2-VTBS-7-12 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Tabular description 3) | AD 2-VTBS-7-13 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Tabular description 4) | AD 2-VTBS-7-14 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Tabular description 5) | AD 2-VTBS-7-15 |
|
Standard Arrival Chart - Instrument (STAR) - ICAO - RNAV RWY 01L/01R - DOLNI3D EASTE3D LEBIM3D NORTA3D WILLA3D (Waypoint list table) | AD 2-VTBS-7-16 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 01L CAT II | AD 2-VTBS-8-1 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 01L CAT II (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-2 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 01L CAT II (Fix and point list table) | AD 2-VTBS-8-3 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 01R CAT II | AD 2-VTBS-8-5 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 01R CAT II (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-6 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 01R CAT II (Fix and point list table) | AD 2-VTBS-8-7 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 19L CAT II | AD 2-VTBS-8-9 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 19L CAT II (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-10 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 19L CAT II (Fix and point list table) | AD 2-VTBS-8-11 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 19R CAT II | AD 2-VTBS-8-13 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 19R CAT II (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-14 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - ILS or LOC z RWY 19R CAT II (Fix and point list table) | AD 2-VTBS-8-15 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 01L | AD 2-VTBS-8-17 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 01L (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-18 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 01R | AD 2-VTBS-8-19 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 01R (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-20 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 19L | AD 2-VTBS-8-21 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 19L (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-22 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 19R | AD 2-VTBS-8-23 |
|
Instrument Approach Chart - ICAO - RNP RWY 19R (Tabular description) | AD 2-VTBS-8-24 |
|
Bird concentrations in the vicinity of aerodromes | AD 2-VTBS-9-1 |